Biotin for hair loss: benefits and side effects
By Prof. Dr. Soner Tatlidede 2022-10-25
Using biotin for hair has been common since many years due to its benefits and qualities; it is commonly used in cosmetic treatments to treat problems such as dermatitis, or weak nails and hair. But, what does biotin do for hair? What are the benefits of biotin? Is biotin good for hair loss? If you are looking for information about a hair transplant cost in Turkey to put an end to your hair loss problems, you should know that biotin can help your hair. But, how? Don´t miss what comes next to learn more about it.
What is Biotin?
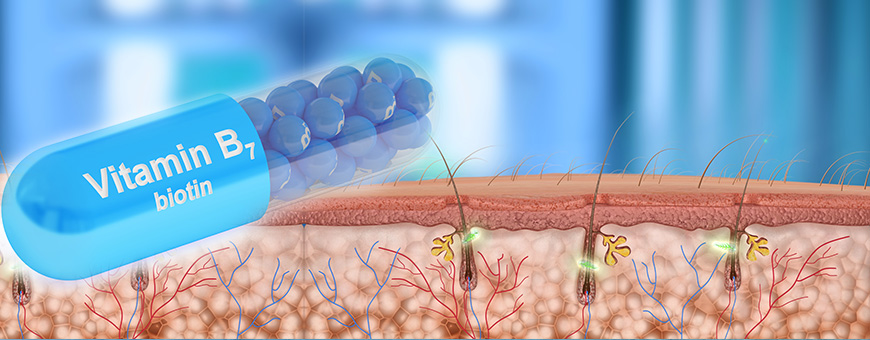
Biotin, also known as vitamin B7 (and formerly as vitamin H), is a water-soluble vitamin who plays an important role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fatty acids, purines and some amino acids like valine and isoleucine. Biotin is a vitamin considered essential for biochemical process through which cells metabolize nutrients.
Biotin can be found mainly in food: our body needs biotin in order to convert certain nutrients into energy, so that our body can use it. Like all other water-soluble vitamins, biotin is not stored in the body; our intestinal bacteria produce biotin, but it´s not clear if it can be absorbed by our body in some way.
In addition, biotin plays an important role in building our body; for example, our hair and nails need biotin to have a stronger structure: this vitamin helps in the creation of keratin, an essential protein in the body, and a cornerstone in making up our hair, skin and nails.
Biotin for hair: what are the benefits?
So, what are the benefits of biotin for hair? Does biotin prevent hair loss? Among biotin benefits, this vitamin favours blood circulation, including in the scalp, contributing to nourishing follicles and, therefore, to hair growth. Biotin will not just allow us to have a healthy and well-nourished scalp: it will also provide strength and elasticity to our hair, making it shiny, too.
Taking that into account, it becomes clear that lacking this fundamental vitamin will have consequences for our hair, which will become thinner, more fragile and brittle, dull and lifeless; in addition, hair will fall out more, and its growth will slow down. That is why it is so important that this vitamin is present in our diet.
In fact, in one study carried out in the Harvard University, biotin was considered one of the main nutrients for preserving hair strength, texture and appearance. This is the main reason why the use of biotin for hair loss is quite common in many products related to hair health (especially those who work on hair growth and thickness), or targeting alopecia symptoms. For example, it´s easy to find biotin and collagen shampoos, combining both ingredients to promise a thicker, stronger and growing hair.
Foods rich in biotin
So, what are those biotin-rich foods for hair growth that we can take? Basically, there are two main groups of foods with biotin:
Foods rich in biotin of animal origin:
- Organ meats like the liver or kidney
- Egg yolk
- Oily fish
- Dairy products
Foods rich in biotin of vegetal origin:
- Nuts, like almonds and peanuts
- Soybeans and other legumes
- Bananas
- Whole grains
- Cauliflower
- Mushrooms
- Sunflower seeds
You probably take enough amount of biotin for your body through the food you eat every day, but in case you want to increase your biotin intake, or if you do not eat enough quantity, there is also the option of taking biotin tablets or supplements for hair.
What causes biotin deficiency?
Although biotin deficiency is rare, however it occurs, especially for people with metabolic problems. Biotin deficiency may be a result of malnutrition, losing weight in rapid rate, and many other different medical conditions; for example, it´s known that biotin levels are lower in alcohol addicts that in other people; biotin levels are lower in athletes, epilepsy patients, elderly, and sick people who had a part of their gastrointestinal tract removed, too.
There is some evidence which shows that diabetes may cause low biotin levels, too. Pregnant women have also lower levels of biotin because of the increased demand for vitamins; they are more likely to have biotin deficiency, and studies have shown that 50% of pregnant women develop a deficiency in this vitamin. Following a diet based on white eggs for a long time causes biotin deficiency, too; this is due to avidin, a protein that exists in big amounts in raw white eggs and that binds with biotin, reducing thus its bioavailability.
What medications reduce biotin levels?
Taking many medications may also reduce biotin levels in the blood, which may affect your biotin requirements. If you are using some of the following medications, you should ask a pharmacist or a doctor in case you need to take biotin:
- Carbamazepine
- Phenobarbital
- Phenytoin
- Primidone
This list is not complete: there are other medications that may interact with biotin, like vitamins and herbal products. There are no side effects recorded for biotin in doses up to 10 mg per day. Anyway, always tell your doctor about any unusual symptoms you may feel during your biotin treatment.
Deficiency symptoms
There is no laboratory analysis good enough to identify biotin deficiency; therefore, this condition is diagnosed by its symptoms, including hair loss (it often includes losing hair pigmentation, according to studies), red rash around the eyes, mouth and nose, and conjunctivitis. The most distinguishable symptom of biotin deficiency is swollen face with irregular fat distribution, and red rash.
Neurological symptoms include depression, fatigue, hallucinations, and numbness in hands and feet. Chronic biotin deficiency or recurrent deficiency may also lead to problems in the immune system, and increase the risk of developing fungal and bacterial infections.
How should I take biotin supplements?
Biotin supplements are usually sold in capsules and include other additives for hair, such as collagen or hyaluronic acid; however, due to the proliferation of this type of pills and supplements, we must warn you about the risks of consuming them without the supervision of a specialist: if not, you could exceed the maximum recommended daily dose – which is 30 μg (micrograms, or mcg) a day in adult women - and then, side effects will appear.
Since biotin deficiency is considered rare, the FDA didn't set a limit for a recommended dosage of biotin. Thus, the dose may vary depending on the person, age, sex, and overall health condition. However, experts advise the following dosage of biotin supplements:
- Patients with an age of 10 or older should take biotin dosage between 30 and 100 mcg per day.
- Infants and children should get:
- - since birth until 3 years: 10 to 20 mcg
- - age of 4 to 6 years: 25 mcg
- - age of 7 to 10 years: 30 mcg
- Women breastfeeding or pregnant: 35 mcg
Note that biotin supplements, if taken under medical supervision, are generally safe; but, they can interfere with some lab results. Some people also choose the option of taking biotin injections, which must be always performed by a skilled medical expert, and that have shown in some cases an increase in hair growth and thickness.
How long does the treatment take until results appear?
Although studies on this issue are limited, two studies done in 2012 and 2015 showed that improvements after starting a treatment with biotin supplements may appear once at least 90 days have passed. These improvements include an increase in hair growth and shine.
Biotin and its side effects
Although the benefits of biotin for hair are well known, it is also important to understand the dangers and side effects of using biotin for hair growth if we exceed the maximum recommended dose; if this happens, symptom and side effects include:
- Nausea (especially during the first stages)
- Stomach problems and diarrhoea
- Allergic reactions (including swelling of the face and throat, rashes on the body, etc)
- Appearance of acne on the lower part of the face
- Increased risk of abortion in pregnant women
Other benefits of biotin:
Despite these aforementioned side effects, in some patients diagnosed with certain diseases it may be advisable - always under medical supervision - to consume higher doses of biotin, since it may provide other benefits for them such as:
- Condition improvement in people suffering to multiple sclerosis (MS)
- Reduction of nerve pain in people with diabetes
- Reduction of blood sugar levels in patients with diabetes (if combined with chromium) for
- Decrease in muscle cramps caused by dialysis
- Shortening of altered mental status and motor control problems episodes, in patients with basal ganglia dysfunction (if combined with thiamine)
Does biotin help hair growth?
The truth is that there is still controversy on the effectivity of using biotin for hair growth; although there are several studies that would support the results of using biotin supplements to stimulate hair growth, some argue that biotin products used in laboratory tests and studies include other components that can also affect hair growth levels, even more than biotin itself.
However, evidence seems to be stronger about the benefits of biotin supplements to stimulate hair growth and prevent hair loss in people with temporal or chronic biotin deficiency; this is certainly supported by studies that have found a clear bond between hair loss and biotin deficiency.
Therefore, in these cases there is strong enough evidence that taking biotin supplements to correct the deficiency, can help to restore hair health and growth. Anyway, we must always bear in mind that hair loss can be a consequence of multiple factors, so we should never focus just on the biotin, whether we do so as a cause of hair shedding, or as a solution.
Using biotin after a hair transplant
So, does biotin help stop hair loss? While there is still controversy on the issue, the fact is that many doctors and hair specialists recommend using biotin after getting a hair transplant, at least during the following 6 months after the surgery, to ensure that new hair grows quicker and stronger. Many experts suggest that using not just biotin (B7), but other B group vitamins such as B12, improves health and quality of the new growing hair after getting hair implants. Biotin also helps to control inflammation during the hair surgery.
In sum, we can say the use of biotin for hair has many benefits, specially when administered in the recommended dose and under medical supervision. Remember that at Clinicana we are specialists in all types of hair treatments, and the best-rated clinic: just take a look at the reviews on hair transplant in Turkey left by our patients, and find out what makes the difference. What are you waiting for? Ask for a free consultation, and see what we can do for your hair. No obligations!
c